The white landscape of sign language interpreting can inhibit Students of Color in their pursuit of becoming sign language interpreters. Jasmine Solis examines some of the reasons language learning and cultural exploration may take a back seat to self-preservation.
Introduction
An individual’s confidence is a crucial element that influences self-esteem, performance, character, and one’s ability to navigate spaces. In the field of sign language interpreting, an individual’s confidence has a great impact on their perception of their signing ability and their interactions with the Deaf Community and peers. In this study, a lack of confidence was a prevalent theme whether explicit or implicitly stated by students. All students expressed not having confidence in their signing skills and/or were self-conscious of their language use. Many narratives provided by students reflected heightened levels of anxiety in the classroom, interpreting situations, and during interactions with peers and the Deaf Community.
Why is there a Lack of Confidence?
Evaluating the possibilities as to why there is a lack of confidence present amongst People of Color (POC) students is the first step in unpacking the issue. In a study conducted by Erica West Oyedele (2015), a current Black interpreter in the field, she hypothesized that the reason for disparities in the field was related to the fact that sign language interpreting programs do not properly address the issues of multiculturalism because of insufficient cultural competence. Participants in her study expressed a desire to have more people who share their racial and ethnic background in the field of interpreting; therefore the burden to assimilate is frequently placed on the interpreter/transliterator of color and not on interpreters of the majority culture (Oyedele, 2015).
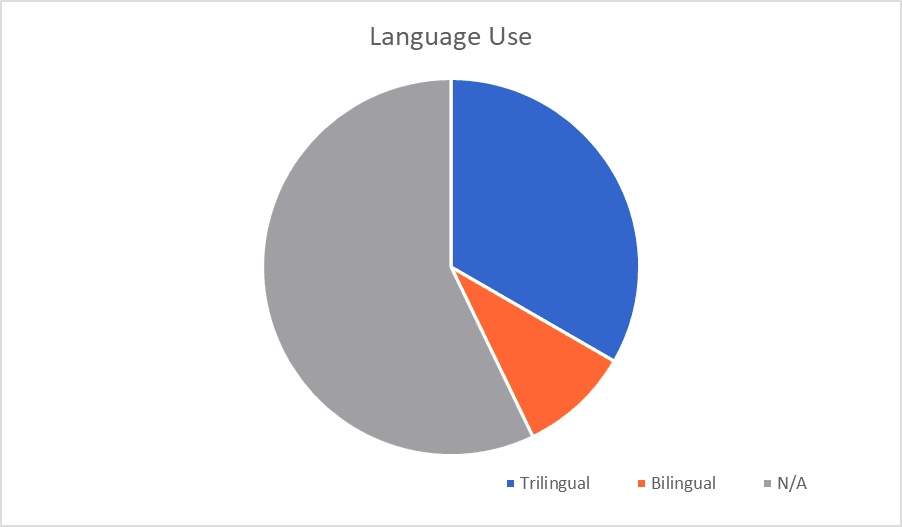
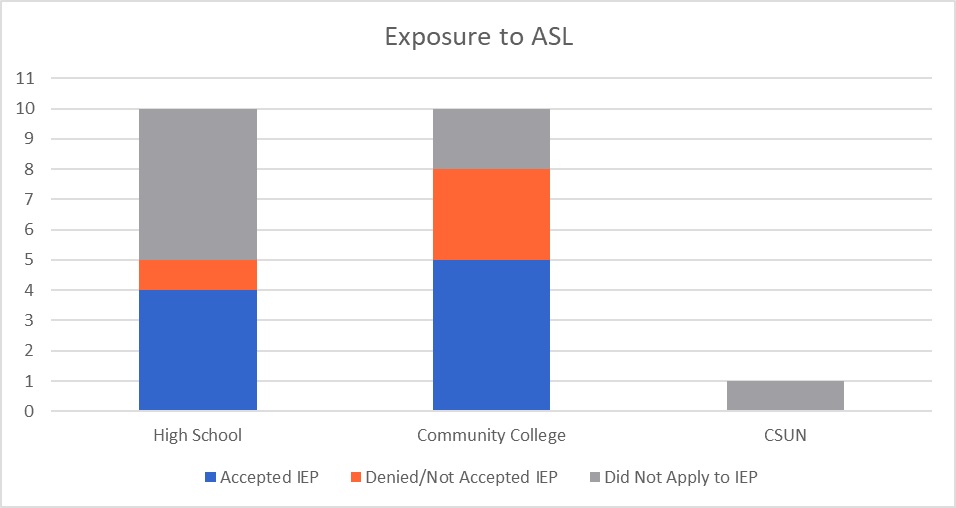
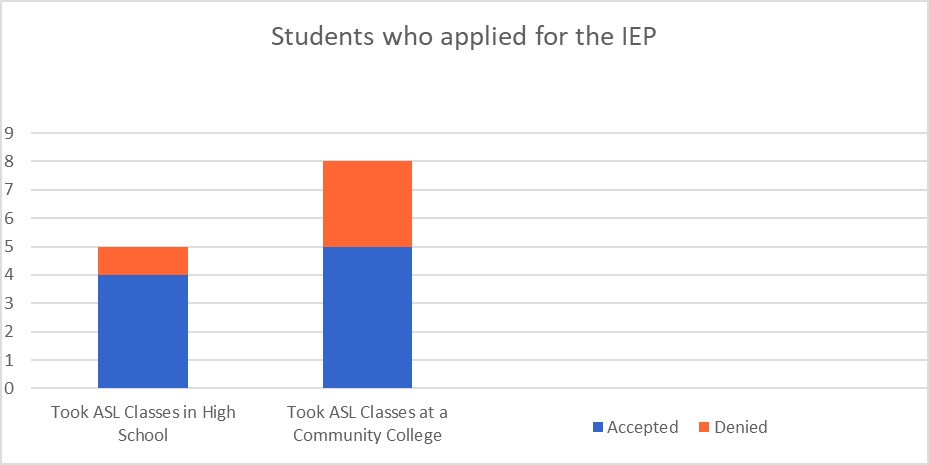
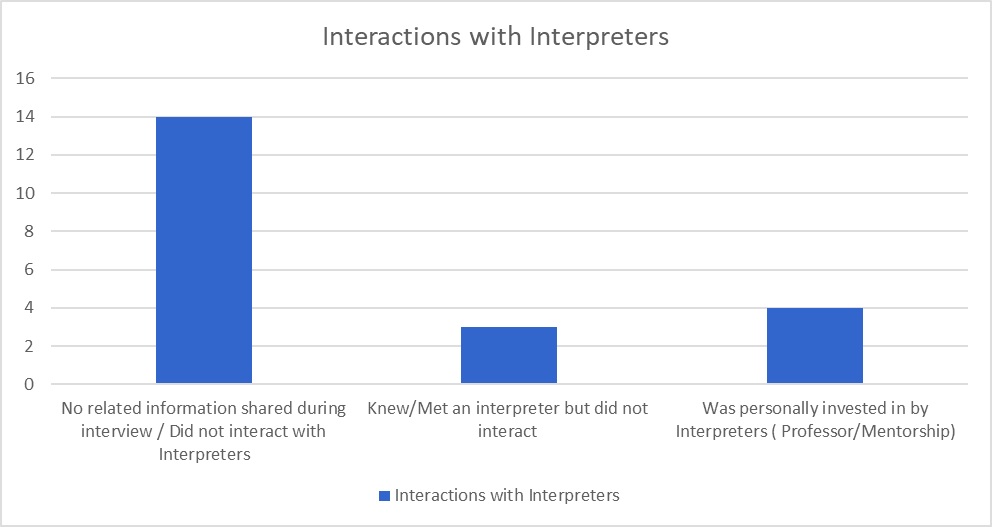
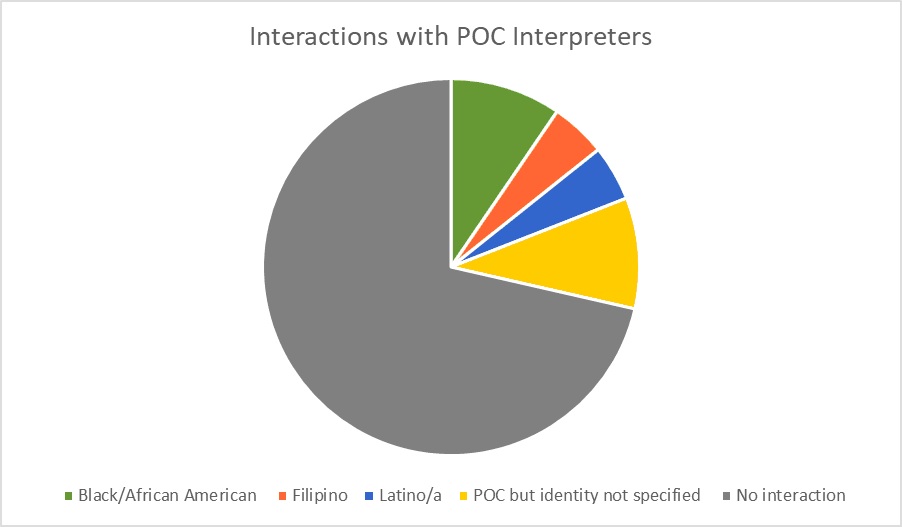
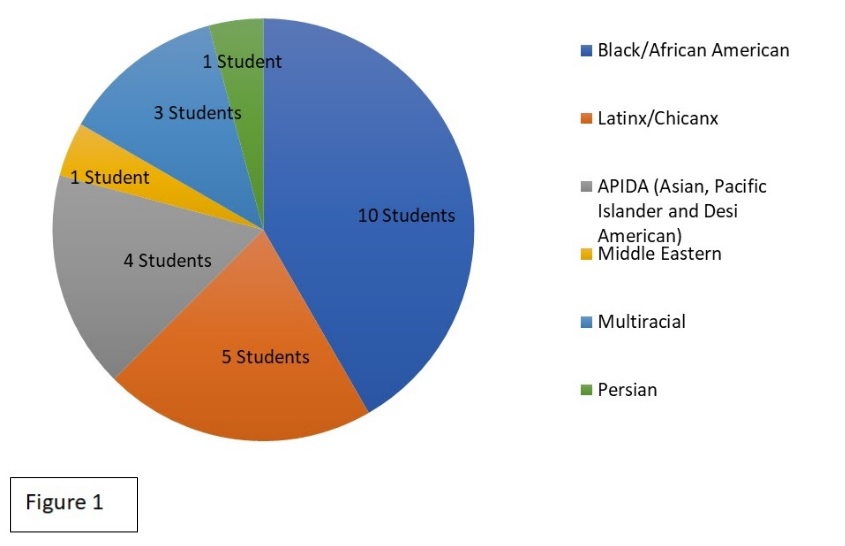
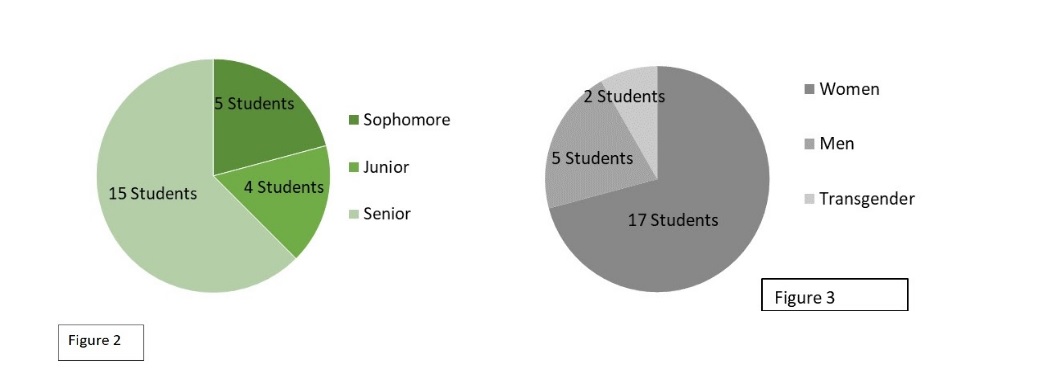
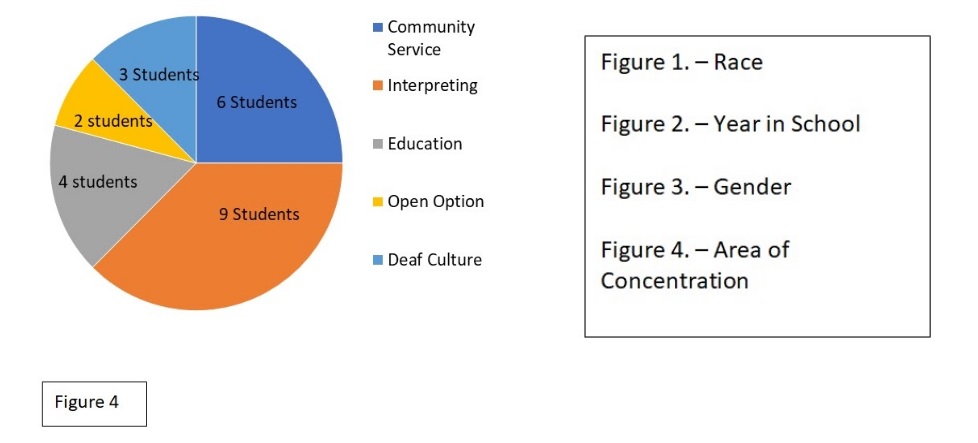
The data chart below responds to the atmosphere of the interpreting programs and the accessibility that students had with mentors, support, and cultural awareness, regarding POC. When considering this data, having confidence in a space that does not reflect your identity is challenging. Our study also revealed parallel feelings of an inability to connect revealing that change is needed in regards to how students interact because it influences confidence.

Classroom Environment and Interactions with Peers
In an environment that persistently evokes competition, self-consciousness, and self-analysis, anxiety increases. Students expressed not having enough confidence or trust in their signing ability as the main reason for not applying to the IEP. One Latina female in her interview expressed,
When I first got in [accepted to CSUN], I had to retake ASL. ‘Does that mean I’m not good enough?’ And I started looking down on myself. ‘Okay, I’m probably not good enough. But I still kept positive and kept trying. I applied for the Interpreting Educational Program, and I was confident. But then got turned down, and started to feel less of myself. Family and relationship problems kicked in and made me feel very down, and by spring 2014, I stopped being involved with the Deaf Community…In spring 2015, I reapplied (and was denied) and again felt like crap, and then I [looked at] what students applied, ‘is it race? Because I’m female? Am I not good enough?’
The desire to be around other Students of Color also affects an individual’s involvement in the field and their aptitude. Minority students are continuously aware of their minoritized status; there is implicit racial bias surrounding their ability to succeed in specific environments. The stigma that has been created due to the achievement gap between the majority and minorities in Education creates a false belief that minority students are unlikely to succeed with the exception of a select few. Since the white majority currently dominates the field of sign language interpreting, making up 88% of RID, many Students of Color do not feel welcome (RID.org). When a POC steps into a predominately white space or career field, they are automatically noticed, positively or negatively, and experience a heightened level of anxiety because they are aware of their otherness. Their response to reduce anxiety is often to avoid these spaces completely which leads to low numbers of IEP Students of Color and ultimately results in low numbers of Interpreters and Transliterators of Color.
Students also expressed increased discomfort in the classroom when they were the only POC and felt a responsibility to represent the community. The racial demographic of the IEP at CSUN at the time of the study consisted of one female black student. During her interview, she revealed feeling as though all eyes were on her, all the time. She reported she was either tokenized in the classroom for the “Black Perspective” or did not want to have her success, or lack thereof, to be connected with her racial identity. Willingly placing oneself in an environment where one’s minority status is tokenized can diminish confidence and increase anxiety, which influences performance. Students of Color have been mistreated in the classroom environment for extended periods of time throughout their lives and many narratives expressed this phenomenon. A Pacific Islander transgender male student stated in his interview, “You can tell [by the way a] teacher look at you…I get a lot of looks from teachers, and I expect that outside of the classroom, but not in the classroom.”
Interviewees reported feelings of invisibility because they were not called on in class, were ignored by peers during group work, and /or their input was not being valued. All of these experiences affect confidence and reinforce the achievement gap. Another aspect of invisibility was due to lack of representation in curriculum, in places of administration, and in classroom discussions. This notable absence greatly affected their desire to become a member of a community while also affecting their confidence in the field, leading to a lack of involvement in the Deaf Community. Students expressed not feeling welcome or comfortable in the classroom environment, which then affected their involvement in the Deaf Community. Many interviewees, as Students of Color, felt it was difficult to relate to their white peers who were the majority of their classmates, and they also reported they struggled to meet Deaf POC on campus. If a minority presence is not acknowledged, students will not feel that they are welcome. A Male student expressed in his interview, “No one will sit next to me unless it is the very last seat and it’s always been that way. Someone will walk across the room before they sit next to me.”
Socialization with the Deaf Community
Lack of involvement with the Deaf Community was deeply connected to a lack of involvement with peers in the classroom. Socializing with the Deaf Community is crucial in developing first-hand cultural knowledge and improving ASL skills. The importance of socialization is known amongst students, however, when looking at student involvement in the Deaf community among the 21 students surveyed, 57% of students expressed little to no involvement. A black female student stated, “I have little to no interaction with the Deaf community. I’m very quiet and keep to myself and I’m okay with just watching.” Of the nine students who expressed involvement, responses consisted of having strong friendships with Deaf individuals, attending a Deaf church, involvement in Deaf clubs or sign language communities, and living in close proximity to or having Deaf roommates. Students who attended Deaf events regularly saw a continuous exposure to ASL, which progressively improved their connection and confidence in working with and being a part of the Deaf Community. Having a connection with an individual who is already established in the Deaf community can be very beneficial for Students of Color. Lower anxiety levels are common when students are in familiar company as it creates a safer, more comfortable environment which allows for the opportunity to develop their ASL skills and confidence. Networking is very important in the Deaf Community therefore, without a connection through friends or colleagues, involvement becomes a challenge.
Interviews revealed that students who were not regularly involved with the Deaf Community experienced anxiety when going to Deaf events or felt that they would be rejected because of their signing skill which often deterred their attendance. The anxiety, stemming from a lack of confidence in skills, influences an individual’s comfort level in different spaces, thus affecting interactions with the Deaf Community. The desire to interact with Deaf individuals is there, but the fear of rejection by the community is a huge deterrent. This creates a detrimental cycle of low exposure and interaction with the Deaf community which impedes language development and the acquisition of real-world cultural knowledge that can only be learned outside of the classroom. The social barriers to becoming comfortable in these interactive spaces are increasingly problematic. A black female student stated,
I know that I don’t have a firm grasp on ASL. I know I don’t always have a firm grasp on how to convey a message. I can’t understand fingerspelling for my life. I put up a barricade because I don’t want to be made fun of. It’s a catch 22. You need to go interact to get better but I don’t want to go interact because I don’t want to be made fun of. And then you get to the point where it’s too far gone for you. You should have been doing this (going out to Deaf events) two-three years ago. I feel pressure from my peers. ‘You’re not at this level yet. We’re here, why are you not here?
Students of Color have been continuously demoralized and degraded in public spaces, leading to a lack of confidence in public. Some students, when faced with this adversity, are able to overcome these feelings and will willingly place themselves in social interactions because they understand the benefit it has on developing their ASL skills, but we cannot expect and should not expect all POC students to respond in this manner. Creating an authentic space versus a safe space is what departments should strive for to develop student’s confidence. We cannot guarantee that spaces will be safe; but we can strive to create an authentic space where opinions can be voiced and objections or agreements can be made for the purpose of growth in character, ability, and success.
Conclusion
The time dedication being involved in the deaf community was difficult but important. I had a daughter in my second semester at El Camino and had to reevaluate my game plan. I still had a desire for interpreting but felt that maybe doing something with advocacy was better because I didn’t have that additional support. Trying to juggle my career and daughter minimized my time. I had to compromise my dreams and time to socialize to take on that motherly role. – Black Female Student
The narratives that came out of the interviews reveal common feelings expressed by POC students. The feelings of incompetence, students wanting to socialize but fearing rejection, a desire and passion to succeed, and experiencing and internalizing failure are common among students. In the sign language interpreting space, motivation, encouragement, and mentoring are greatly valued because Interpreters of Color are very far in between. Any information that can be beneficial or support a Student of Color is crucial. Many POC feel that they are at fault for their rejection. They feel that if they are critiqued, they are not good enough. They struggle with separating their personal identity from their career.
In order to continue this discussion, here are some questions to consider:
- What role can mentors (sign language or non-related mentors) play in building a student of color’s confidence?
- How can faculty identify and support students who are experiencing anxiety in the classroom and having confidence with “being in the limelight” during interpreting situations?
- Knowing that the student populations in IEPs are extremely white-centric, how do we build alliances across different communities so that these programs can become much more supportive environments?
*We would like to thank and acknowledge John Pak, M.Ed., for the time and energy invested in the translation and ASL video work presented here.
References
West Oyedele, E.(2015), “Persistence of African-American/Black Signed Language Interpreters in the United States: The Importance of Culture and Capital” Dissertation.
Other Contributors to this Series:
Lissa Ramirez-Stapleton
Dr. Lissa D. Ramirez-Stapleton is an associate professor at California State University Northridge in the Department of Deaf Studies and core faculty for the Educational Leadership and Policy Studies program. Her research focuses on equity and access, identity development, and the educational history of Deaf students, faculty, and staff with a particular interest in the intersections of race, gender, and disability. www.drlissad.com
MJ Jones
MJ Jones (pronouns: they/them/theirs), a Southern California native, currently resides in the Washington, D.C. area. MJ’s intersectionalities include Black, first-generation Filipinx, masculine of center, sighted, and hearing. After graduating from California State University, Northridge with a B.A. in ASL-English Interpreting and a minor in Queer Studies, MJ graduated with their M.A in International Development at Gallaudet University. They are currently an adjunct professor at Gallaudet University and a Full-Time Staff Interpreter with Vital Signs, LLC.
Will Garrow
Dr. Will Garrow, Ph.D. (pronouns: he/him/his) is from upstate New York, where he was first introduced to the Deaf Community through his career as a professional snowboarder. All of his degrees are from Gallaudet University with a Bachelor of Arts in Deaf Studies, a Master of Arts in Linguistics, and a doctorate in Linguistics. As a faculty member at California State University, Northridge, his teaching mainly focuses on how oppression works in American society, Deaf Culture, and ASL Linguistics. When Will is not teaching, he can be found either on the snow in the mountains or splatting balls in the racquetball court.